
Battle of Shirimni(Battle of Lake Palakazio) |
year: 102111 September 1021 |
| A difficult victory of the Byzantine army over the Iberians | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
|
enemy: Iberians (Georgians)
|
location: In the area of lake Cildir in NE Minor Asia, in modern Turkey, near the borders with Georgia and Armenia
|
accuracy:
●●●●●
|
|
battle type: Pitched battle |
war: Iberian war |
modern country:
Turkey |
| ▼ The Byzantines(emperor: Basil II Bulgaroktonos) | ▼ The Enemies | |
| Commander: | Emperor Basil II | Ruler of Iberia Giorgi I |
| Forces: | 40,000 | Outnumbered |
| Losses: |
| Background story: |
| In the year 1000, Emperor Basil II was in southern Asia Minor, in the region of Tarsus, where he had spent the winter after his campaign against the Arab Fatimids. It was there that he learned of the death of the Iberian (=Georgian) David III, ruler of the state of Tao (or Taik) in northeastern Asia Minor, in the Caucasus region. David, who was honored with the Byzantine title of Kouropalatis, had played a role in the civil war of the beginning of the reign of Basil, when he had supported the rebel Vardas Phokas. After the failure of that mutiny, David declared submission and had promised, that his state would bequeath it to Byzantium. So after his death, Basil rushed to the area, directly from Tarsus, to secure the inheritance. This was done without any particular problems from the Iberians and, thus, a fairly large new area was annexed to Byzantium, which later, after 20 years, would become the Iberian thema. 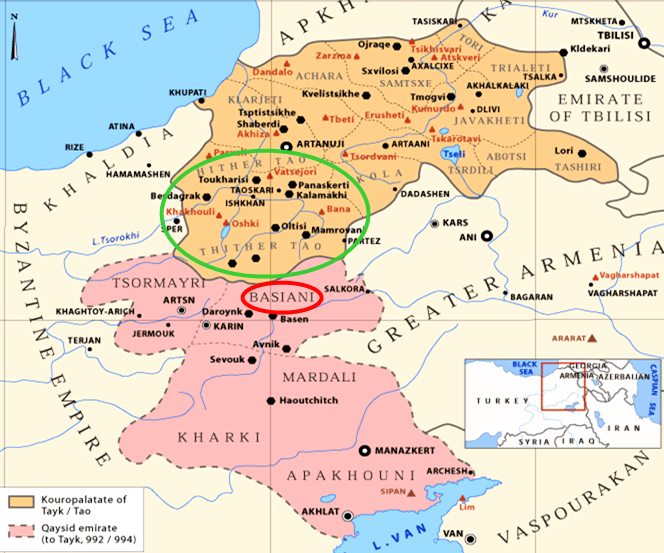 The Tao/Taik region in green outline In general, the regions of Iberia and Armenia were divided into many small independent hegemonies that never posed a serious threat to Byzantium. But around that time, the king of Abasgia (Abkhazia) Bagrat III (Pagratios for the Greeks) managed to conquer or annex various principalities south of the Caucasus (mainly Iberian and Armenian) and form a large “kingdom of Iberia and Abasgia”. After his death, his successor George I (also known as Giorgi or Crocri), implementing his father's ambitious plans, in 1014 violated the agreements with Byzantium and encroached on Byzantine lands by annexing the Taik region, that is, the old principality of Kouropalatis David (who was the uncle of George I). At the same time, the Iberians formed an alliance with the “Mad Caliph” of the Arabs, Al-Hakim. Basil II did not react immediately to this offense, as he did not want to distract himself from the war against the Bulgarians. Much later, in 1021, the always unforgiving Basil II, decided to deal with the Iberians (it may have played a role that Al-Hakim disappeared from the face of the earth that year – literally). So the sixty-three-year-old emperor led a large army of 40,000 men, 5,000 of whom were the Varangians, and encamped in Asia Minor. In order not to lose the advantage of surprise, he did not reveal to his officers the real purpose of the campaign. Everyone had the impression that they were heading to Antioch. The army moved quickly and encamped in the area of Theodosioupolis (Erzurum). From there, the Iberian rulers were notified of the arrival of the emperor who was waiting for them to pay their respects. George, however, refused to go. Giorgi's contemptuous attitude angered the emperor and ordered the destruction of the city of Okomi (now, Ugumi). George in turn destroyed the city of Okhtik (for reasons unknown) and began to retreat to the east, in order to avoid confrontation with the powerful Byzantine army. |
The Battle: |
 Basil II Only a part of the Iberian army was involved in the battle as the rest had advanced. The Iberians fought bravely and proved to be a difficult opponent. The Byzantines were repulsed repeatedly, but in the end, they prevailed thanks to their experience and numerical advantage, while the Iberian cavalry was stuck in the swamps around the lake. Among the dead was the leader of the army of the Iberians, Liparitis. |
Aftermath: |
| It was a bloody battle, but the difficult victory of the Byzantines was indecisive, while a large part of the Georgian army escaped, and then was reinforced with forces from other Caucasian hegemonies and regrouped. The Byzantine army followed them for a while and tried to engage them in battle, but to no avail. Eventually, it returned and retired for the winter to Trabzon, having first looted and deserted 12 provinces of Iberia. The hostilities resumed the following year. |
|
|
